Understanding the types and materials of roofing framing is essential to ensuring the stability and durability of your home. Building a new home or replacing an old, durable roof starts with the right materials and techniques.
This roof framing guide will explore the various types, materials, and step-by-step processes every homeowner should know.
Table of Contents
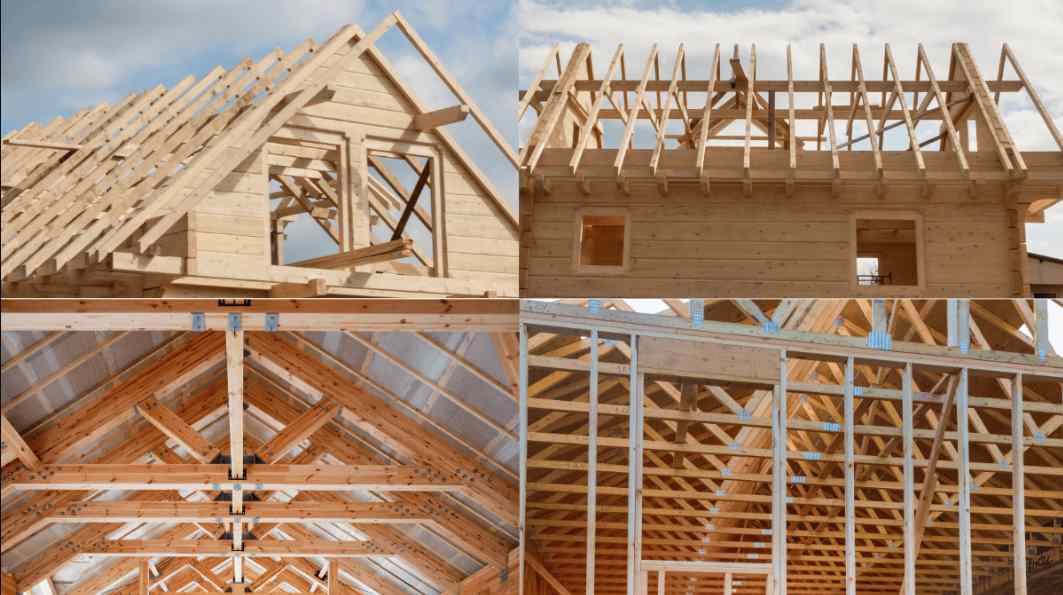
What Is Roof Framing?

Source: Modern-exterior
Roof framing provides a roof system that supports your roof. This system consists of beams, columns, and other elements that transfer the roof’s weight to the walls below. The roof framing design must be strong enough to withstand the weight of roofing materials, snow, rain, and other environmental impacts.
Key Components of Roof Framing
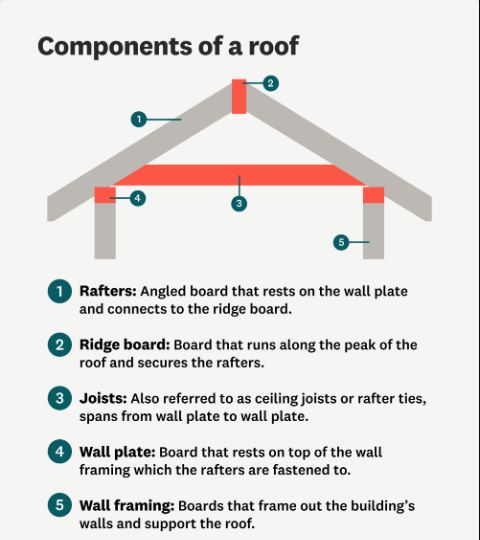
Source: Media.Angi
Roof framing is the backbone of any roof, providing support and stability for longevity. Here’s a quick breakdown of its highlights.
- Rafters: A recessed beam from the ridge to the roof, which supports the roof covering and distributes the weight.
- Ridge Board: The horizontal board at the roof’s peak, connecting and stabilizing the rafters.
- Collar Ties: Horizontal bars attached to bars adjacent to the shell to prevent expansion and provide excellent stability.
- Trusses: Prefabricated structures that provide strength and efficiency for large spans, often replacing traditional frames.
- Ceiling Joists: Horizontal beams that support the roof without expanding walls.
- Fascia Board: Covers roof edge trim rafters and connects gutters for functionality and aesthetics.
- Soffit: Located at the base of the fascia, ventilation is provided to prevent attic drafts and maintain ventilation.
- Purlins: Vertical supports prevent sagging on large roofs and add extra strength.
Each component is essential to maintaining a strong, durable roof and protecting your home from the elements.
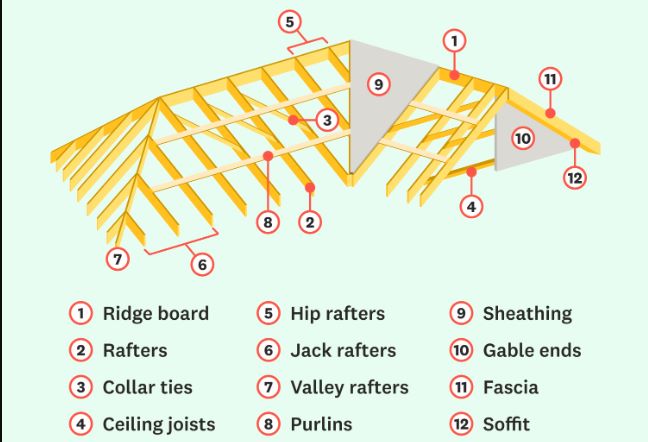
Source: Media.Angi
Types of Roof Framing
Choosing a roof framing type depends on various factors, including architectural style, budget, and building use. Here are some standard roofing framing used in roofing and commercial buildings.
- Traditional Roof Framing (Rafter Framing): In conventional structural roofing, rafters form the skeleton of the roof. Beams or boards support these roof trusses or rafters at the top. This method is suitable for steep and elevated homes.
- Truss Roof Framing: Prefabricated roof frames support the roof structure. This method is cost-effective and reduces installation time. Roof trusses are commonly used in construction because of their durability and efficiency.
- Scissor Truss Roof Framing: Scissor trusses are used in post-built houses. They add height to the interior while maintaining the integrity of the structure.
- Flat Roof Framing: Flat roofs are commonly used in modern commercial buildings or homes. Precise framing techniques are required to ensure smooth and uniform drainage.
Common Roof Designs
- Gable Roof: A typical design with two sloping sides that meet at a ridge. Learn more about the differences between hip and gable roofs and which might be right for your home.
- Hip Roof: A design where all sides slope into the walls, generally creating a more robust structure. Explore the key differences between hip and gable roofs to determine the best option for your home.
- Flat Roof: This design is often used for commercial buildings, so it is important to consider drainage properly. Discover the best flat roof materials to ensure durability and performance for your roofing project.
- Gambrel and Mansard Roofs have sloped roofs on each side, providing additional living or storage space. Learn more about the unique design and benefits of a gambrel roof for your home or barn. Find out how a mansard roof can add elegance and extra space to your property.
Essential Calculations for Roof Framing
To create an effective roof framing plan, several calculations are necessary:
- Span: The distance between two supporting walls.
- Rise: The vertical height from the top of the span to the roof.
- Run: Half of the span measurement.
- Pitch: The slope of a roof, defined as the slope over the run.
These calculations ensure that all components are correctly aligned and that the roof can support the required loads.
Example Calculation
For a roof with a span of 20 feet:
- Run = Span / 2 = 10 feet
- If the rise is 8 feet, then:
- Pitch = Rise / Run = 8/10 = 0.8 (or 8:10)
Understanding roof design is essential for any construction project involving roofing. By knowing the basic components, framing types, and necessary calculations, architects can create a robust and reliable roof that meets aesthetic and architectural requirements.
Key Roof Framing Materials
The materials you choose for your roof framing directly impact the durability and longevity of the roof. Here are some common roof framing materials used in construction:
- Wood: Wood is the most common material used for roof framing in residential buildings. It’s convenient, affordable, and easy to work with. Popular species include pine, fir, and cedar.
- Steel is commonly used in commercial buildings or climate zones. It is stronger than wood but can be more expensive.
- Engineered Lumber: Materials like laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and oriented strand board (OSB) are engineered to achieve superior strength. These products are often used to support others on residential roofs.
- Concrete and Masonry: Concrete is commonly used for flat roofing due to its fire resistance and durability. However, installing and draining it requires special techniques.
The Roof Framing Process
Understanding the roof framing process is crucial for a successful installation. Here’s a general breakdown of the steps involved:
- Planning and Design: A roofing contractor or professional engineer should prepare a detailed roof design that includes calculations for load-bearing walls, roof pitch, and the type of materials to be used
- Construction: Installation begins with measuring and placing ridge boards, followed by rafters or trusses. Then, the roof is covered with plywood and other materials to provide a solid foundation.
- Inspection: Once completed, the building must be inspected to ensure it meets local building codes and is in good standing.
How to Choose the Right Roof Framing Materials for Your Home
When deciding on roofing materials, consider your home’s climate, budget, and overall appearance. For example, wood frames are a good choice for homes in mild climates, while steel may be better suited for homes in areas with heavy snow or wind. A professional roofing contractor can help you find the best roof framing materials based on your needs.
Benefits of Using Trusses in Roof Framing Construction
Roof trusses offer many advantages in roofing, especially for residential buildings. Key benefits include:
- Cost-Effective: Prefabricated roof trusses are less expensive than conventional roofing methods.
- Speed of Installation: Roof trusses are pre-engineered and easily installed, reducing installation time.
- Strength and Stability: Trusses are designed to carry high loads, making them ideal for homes in areas with heavy snowfall or strong winds.
Best Roof Framing Techniques for Residential Buildings
Modern techniques, such as roof trusses and engineered beams, are essential to ensure the strength and durability of roof installations. In addition, make sure your attic is well-ventilated to prevent moisture from building up, which can damage the frame in the long run.
Understanding Roof Framing Design and Its Impact on Your Home
The design of your home’s roof framing affects not only its aesthetics but also its overall functionality. A well-designed frame helps prevent fading, leaks, and poor insulation. Consulting with a professional roofing contractor can help you choose the best design to match your home’s architecture and ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, roof framing is one of the most important roofing elements that affects your home’s safety, durability, and appearance. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to understand roof framing materials or a contractor involved in roof installation, knowing the different roof framing types and the step-by-step process is key to ensuring a successful project. For expert roofing services in Garrettsville, Ohio, consider contacting professionals like Pally Roofing. More experienced professionals will also communicate. There is a commitment to quality craftsmanship.
Pally Roofing is a trusted roofing company in Garrettsville that specializes in roof framing and other roofing services. Their expertise in roof construction and commitment to excellence ensures your home’s roof will stand the test of time. For more information, visit Pally Roofing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Most Straightforward Roof Framing Plan?
A gable roof is considered straightforward roofing framing. It is a basic rectangular shape with two sloping sides that meet in the middle. The simplicity of the design makes construction easier and more economical, making it popular for multi-unit housing.
What Is The Spacing And Span For Roof Rafters?
Roof rafter spacing generally ranges from 16 to 24 inches, depending on the load requirements and roof design. The width or distance of the columns that can be crossed without tension depends on factors such as the materials used, the pitch of the roof, and the weight to be carried. Residential buildings are usually 10 feet to 20 feet wide.
What Are The Two Basic Roof Framing Types?
Roofing frames are classified as rafter framing and truss framing. Rafter framing has individually designed beams that provide structural support, allowing flexibility in the layout. Truss framing, on the other hand, uses prefabricated rectangles, which are quicker to install and provide more excellent stability for larger spans.
What Are The Parts Of A Roof Framing Called?
A roof framing has key properties for strength and shape. The soundboard forms the roof where the columns meet, and the recessed beams supporting the roof form columns. Collars are horizontal elements that connect opposite trick joists near the ridge, while roof joists provide stability and support for the roof below. Trussed, preassembled frameworks sometimes replace traditional columns for efficient and durable construction.
Author
-

With more than 16 years of hands-on experience, Phillip Schmucker is the knowledgeable owner of Pally Roofing. His dedication to superior roofing services has earned him a reputable place in the industry. Phillip also shares his extensive expertise through writing, providing readers with practical tips and professional advice on various roofing topics. Follow him on LinkedIn.
View all posts






